What will you learn from this article?
- Main Part of Two stroke SI and CI Engines.
- Concept of Working of two Stroke Spark Ignition (Petrol) and Compression Ignition (Diesel) engine with its applications.
- Advantage and Disadvantages of Two Stroke engine.
In our previous articles, we have learnt about engines types and classification of IC engines. We know both two stroke and four stroke engines are widely use in mechanical industries. As the name implies, two stroke engines have two piston strokes. These engines find application in marine industries and in small vehicles.
Two Stroke Engine:
Principle:
It works on same principle of four stroke engine. When the fuel burns inside the cylinder, it creates a large pressure force which is further use to movement of piston hence movement of crankshaft. It completes two piston strokes during one power stroke. It completes all process like suction, compression, power and exhaust in just two piston strokes.
Parts:
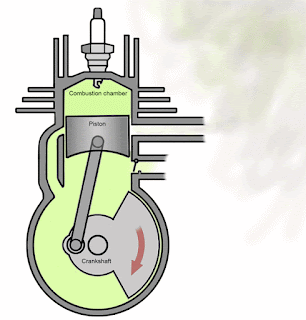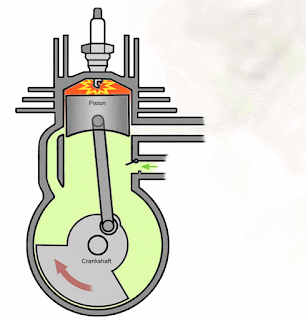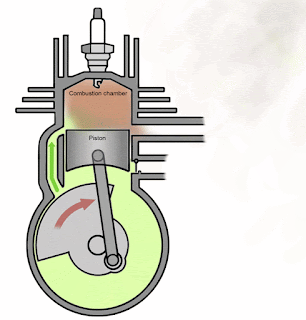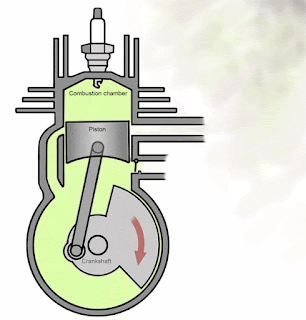
Piston: It moves from BDC to TDC. One stroke of piston is define as movement of piston form one extreme (TDC or BDC) to other extreme (BDC to TDC).
Cylinder: It is same as used in four stroke engine except it does not have valve mechanism. It has two ports on side wall of cylinder.
Crankshaft: It is used to convert reciprocating motion of piston into rotary motion.
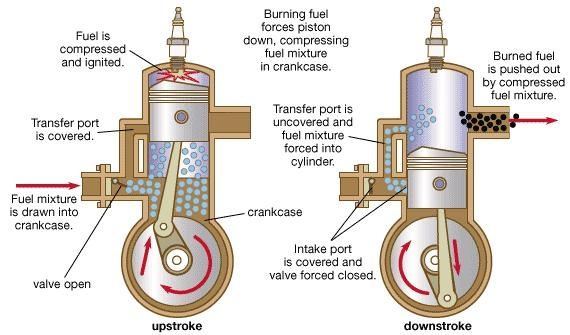
Inlet and Exhaust Port: Two stroke engines contain ports except valves. These ports open and closed due to piston movement. When the piston is moving towards TDC inlet ports opens and when it moves toward BDC exhaust port opens.Transfer Port: These engines contain one extra port which is known as transfer port. It is connected
from crankcase to combustion chamber. Its main function is to supply the charge from crankcase to combustion chamber when piston is moving from TDC to BDC.
Inlet and Exhaust Manifold: These are connected to inlet and exhaust port and regulate the flow of charge and exhaust gases.
Flywheel: It need smaller flywheel compare to four stroke engine because less power fluctuation.
Crankcase: This is the part where crankshaft situated. The inlet port is also connected with crankcase. First charge enters into crankcase and send to combustion chamber through transfer port.
Working of Two Stroke Engine:
Two stroke engines have two types. First one is known as Spark ignition engine or better known as petrol engine, which works on Otto Cycle and other one is compression ignition engine or diesel engine, which works on diesel cycle. Both these engines works on same principle with some fundamental differences. We can summarize its working in following points.
Suction Stroke and Compression Stroke:
Suction means charge drawn into engine cylinder or in case of two stroke engine in crankcase and compression means compressed the previous drawn charge into engine cylinder. In two strokes engines, both these process take place simultaneously. When the piston moves from BDC to TDC, the inlet port opens and partially vacuum created into crankcase which accelerates charge drawn into crankcase. Simultaneously the piston compressed the charge available in engine cylinder or combustion chamber. The exhaust port remain closed during this stroke.
Power and Exhaust Stroke:
In this stroke, piston moves from TDC to BDC. Inlet port remains open for first half of this stroke and closed in other half. Simultaneously, exhaust port remains closed during first half of this stroke and open into second half. Transfer port opens into second half of this stroke.
There is a deflector in engine cylinder which regulate the fresh charge does not exhausted with exhaust gases.
During this piston stroke, in SI engines, spark plug produces sparks. This spark ignited the charge which create a high pressure force. This force moves piston form TDC to BDC. When the piston reaches in middle, the exhaust port and transfer port opens simultaneously. This exhausted burnt gases out from engine cylinder and transfer port supplied fresh fuel-air mixture into engine cylinder from crankcase for further cycle.
In CI engines, injector injects fuel during this stroke. This fuel burns due to heat produced by compression which create a high pressure force. This force moves piston form TDC to BDC. When the piston reaches in middle, the exhaust port and transfer port opens simultaneously. This exhausted burnt gases out from engine cylinder and transfer port supplied fresh air into engine cylinder from crankcase for further cycle.
Application:
- These engines are used in small vehicles like mopeds, scooters etc.
- Small gasoline engines are use for lawn movers.
- It is also used for small electric generator set, pumping set, outboard motor boats.
- Two stroke diesel engines are used for ship propulsion.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Lower cost.
- High power compare to four stroke engines.
- Easy maintenance due to absence of valve mechanism and lubrication system.
- Compact compare to four stroke engines.
- Produce uniform torque on crankshaft.
- More power to weight ratio.
- It is easy to start and simple in mechanism.
Disadvantages:
- Greeter cooling and lubrication oil required.
- These engines are less efficient compare to four stroke engines.
- Lower volumetric efficiency due to lesser time for mixing intake.
- More wear and tear because poor lubrication system.
- It produces high vibration and noisy operation.
- These engine burn lubrication oil with charge so produce more pollution.
Now you should ask yourself these questions?
- What is function of transfer port?
- How to prevent fresh charge exhausted through exhaust port?
- Which engine (SI or CI) is more suitable for two stroke and why?
If you like this article, asks questions in comment box, share it on your social networks and subscribe our website.





What’s ment by Governer.
What’s ment by Torque.