In mechanical engineering and HVAC systems, rotary compressors and reciprocating compressors are the two most widely used positive displacement compressors. Each has distinct construction, working characteristics, efficiency ranges, and applications.
This guide provides a clear, exam-oriented and industry-relevant comparison to help students, engineers, and professionals choose the right compressor.
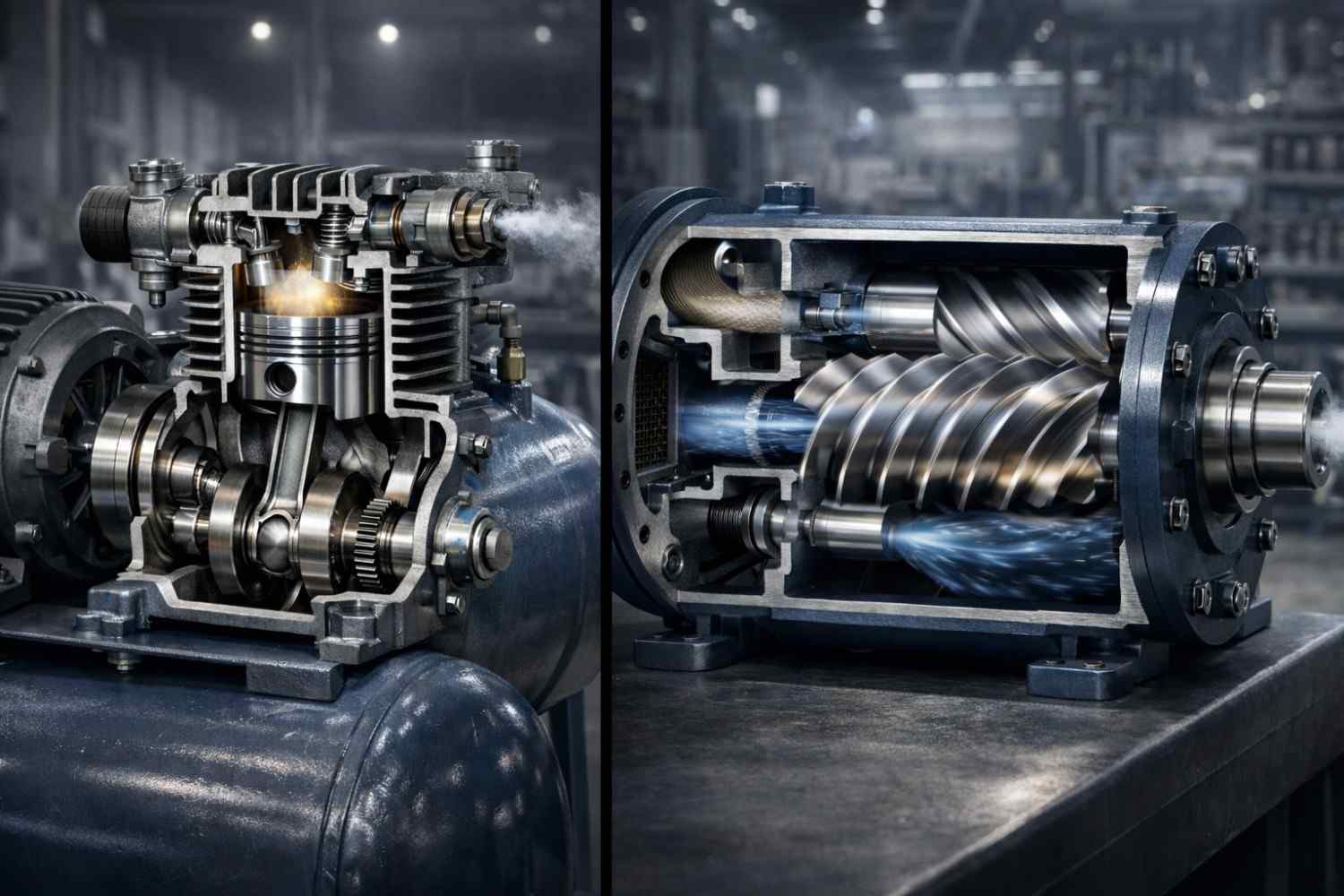
What is a Rotary Compressor?
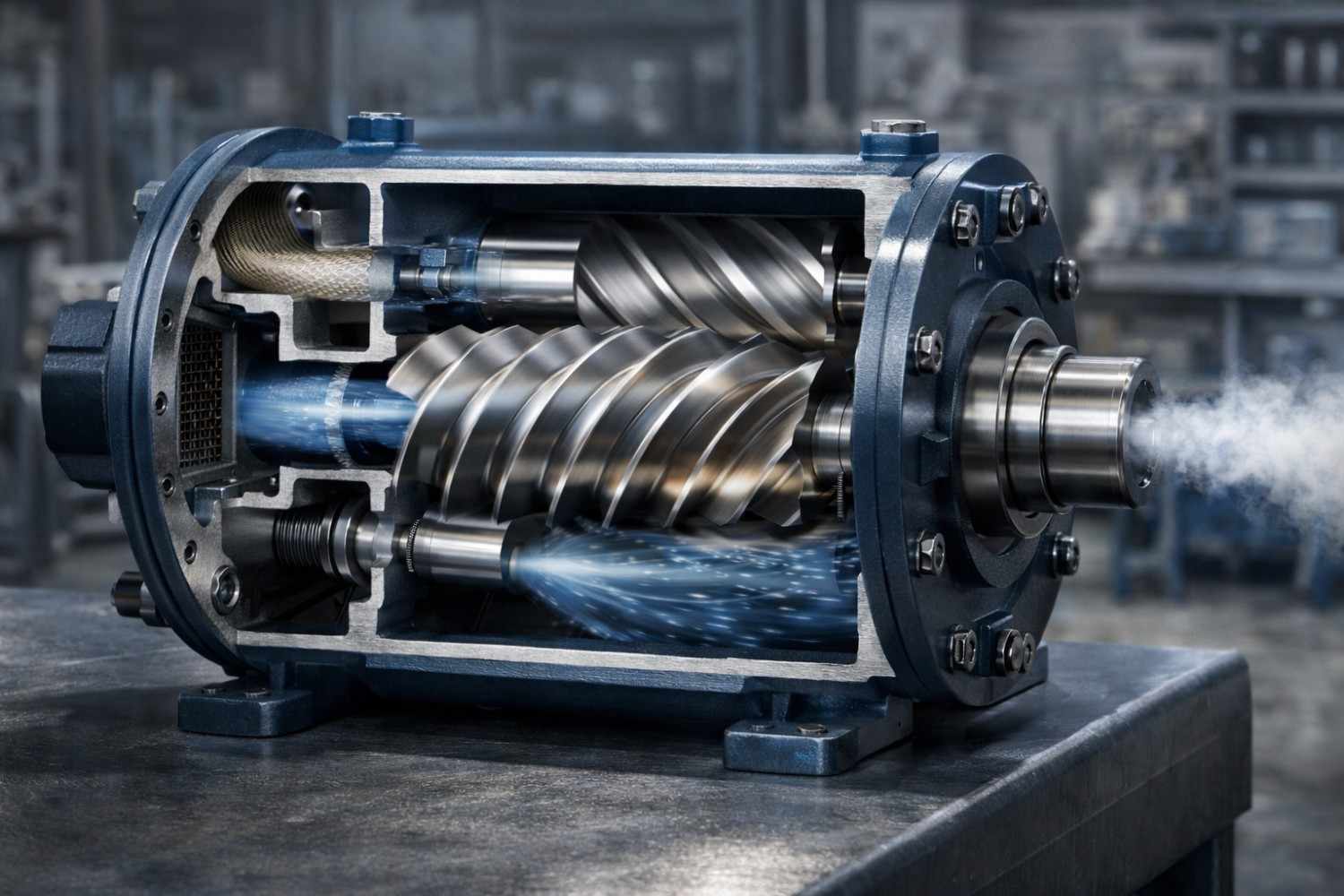

A rotary compressor compresses air or refrigerant using rotating elements such as vanes, screws, or scrolls. Compression occurs continuously as the fluid is trapped and reduced in volume by rotating motion.
Key Features
- Continuous compression process
- Fewer moving parts
- Smooth and quiet operation
- Compact and lightweight
Common Types
- Rotary vane compressor
- Scroll compressor
- Screw compressor
What is a Reciprocating Compressor?
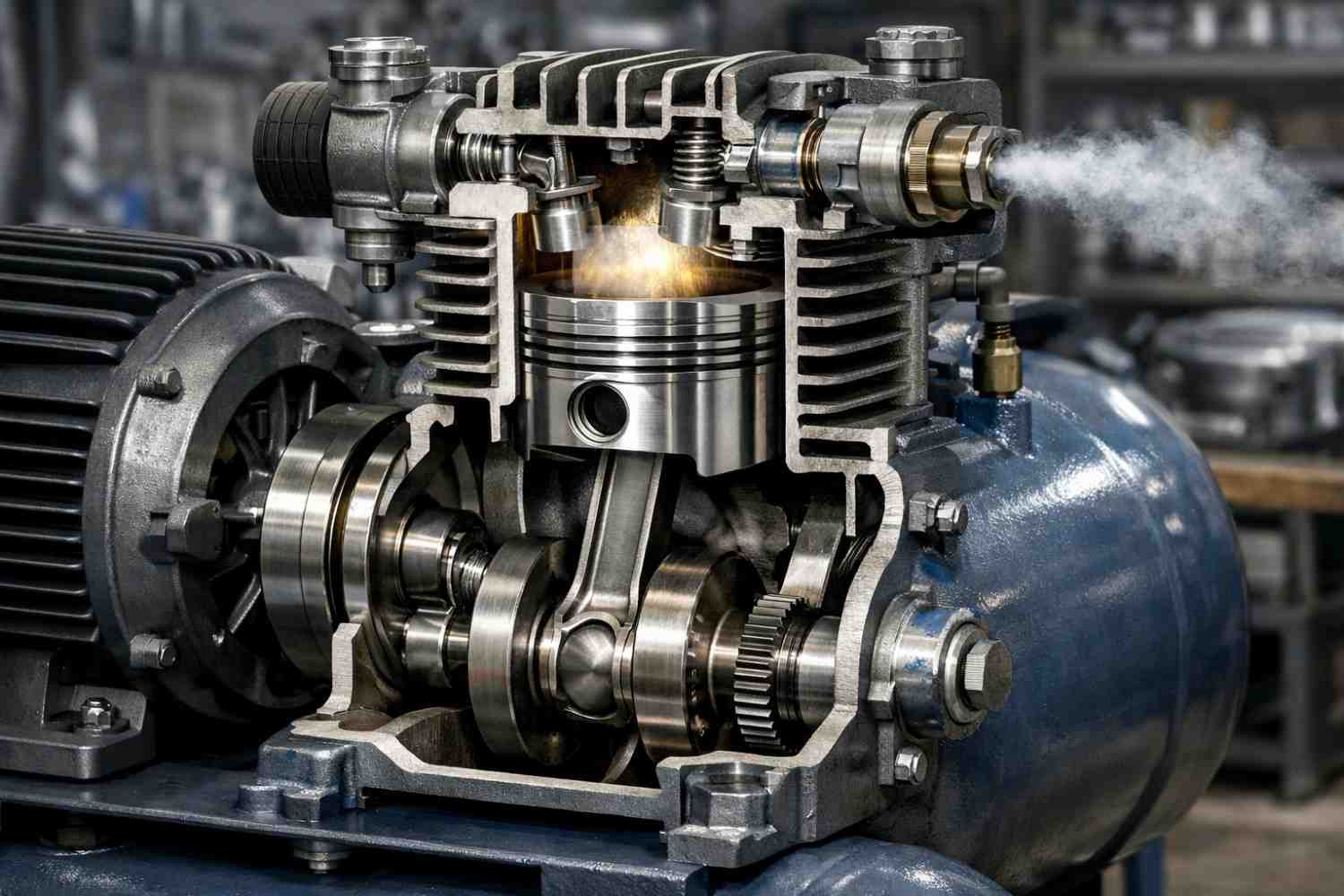
A reciprocating compressor uses a piston-cylinder mechanism where air is compressed by the reciprocating (back-and-forth) motion of the piston, similar to an internal combustion engine.
Key Features
- Intermittent compression process
- High-pressure capability
- Robust and proven technology
- Higher vibration and noise
Common Types
- Single-stage reciprocating compressor
- Multi-stage reciprocating compressor
- Single-acting and double-acting compressors
Rotary Compressor vs Reciprocating Compressor (Comparison Table)
| Parameter | Rotary Compressor | Reciprocating Compressor |
| Working motion | Rotary motion | Reciprocating (piston) motion |
| Compression | Continuous | Intermittent |
| Pressure range | Low to medium | Medium to very high |
| Air delivery | Uniform and smooth | Pulsating |
| Speed | High | Low to moderate |
| Vibration | Very low | High |
| Noise level | Low | High |
| Size & weight | Compact | Bulky |
| Maintenance | Low | High |
| Initial cost | Higher | Lower |
| Efficiency at high pressure | Lower | Higher |
| Lubrication | Minimal | More lubrication required |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Rotary Compressor
Advantages
- Compact design
- Quiet operation
- Low vibration
- Suitable for continuous operation
Disadvantages
- Not suitable for very high pressures
- Higher initial cost
- Limited repair flexibility
Reciprocating Compressor
Advantages
- High-pressure capability
- Better volumetric efficiency
- Lower initial cost
- Easy to repair
Disadvantages
- High vibration and noise
- More moving parts
- Requires frequent maintenance
Applications
Rotary Compressor Applications
- Domestic and commercial air conditioners
- Refrigerators
- Heat pumps
- Small-capacity HVAC systems
Reciprocating Compressor Applications
- Air brake systems
- Industrial air compressors
- Gas compression plants
- Workshops and garages
Which Compressor Should You Choose?
| Requirement | Best Choice |
| Quiet operation | Rotary compressor |
| High pressure | Reciprocating compressor |
| Compact system | Rotary compressor |
| Low initial cost | Reciprocating compressor |
| Industrial heavy-duty use | Reciprocating compressor |
| Continuous HVAC operation | Rotary compressor |
FAQs
The main difference is the working mechanism. A rotary compressor uses rotating components to compress air or refrigerant continuously, while a reciprocating compressor uses a piston moving back and forth, resulting in intermittent compression.
Rotary compressors are preferred for air conditioners and refrigerators because they are compact, quieter, and energy-efficient, making them ideal for continuous HVAC operation.
A reciprocating compressor is better for high-pressure applications such as industrial air systems, gas compression, and pneumatic tools.
Rotary compressors produce significantly less noise and vibration due to fewer moving parts and the absence of reciprocating motion.
At low to medium pressure, rotary compressors are more energy efficient. For high-pressure duties, reciprocating compressors provide better efficiency and performance.
Reciprocating compressors require more maintenance because they have more moving parts (piston, crankshaft, valves) that are subject to wear.
For heavy-duty industrial and high-pressure applications, choose a reciprocating compressor. For continuous, low-noise HVAC systems, a rotary compressor is the better choice.

Which is best compressor for refrigerator 1.Rotary
or
2.Reciprocatory
reciprocating compressor because it is cheap, low maintenance and best suitable for refrigeration requirement.